The pathway towards the lungs is provided by Contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal muscles increases the volume in the chest cavity, which in turn lowers the pressure and draws air into the lungs for inspiration. Quiet breathing, also known as eupnea, is a mode of breathing that occurs at rest and does not require the cognitive thought of the individual. WebThe lung model shows exhalation: When the diaphragm (rubber sheet) moves up, the volume inside the glass jar (thorax) decreases. WebUsing a flow chart, tachycardia, tachypnea; severe accessory muscle use, wheezing during both inhalation and exhalation. OpenStax is part of Rice University, which is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit. breathing. This page titled 20.4: The Processes of the Respiratory System is shared under a CC BY license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Whitney Menefee, Julie Jenks, Chiara Mazzasette, & Kim-Leiloni Nguyen (ASCCC Open Educational Resources Initiative) . The larynx is a 2-inch tube made up of nine cartilage pieces. The internal intercostal muscles are also important in altering the anteroposterior dimension of the chest cavity. These vital organs of respiration inside the thorax are the site responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Contraction and relaxation of the diaphragm and intercostals muscles (found between the ribs) cause most of the pressure changes that result in inspiration and expiration. Except where otherwise noted, textbooks on this site The diaphragm is dome shaped and separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities. When you inhale, your lungs fill with air and then release the air out through your mouth. WebWhy is inhalation an active process but exhalation is passive? We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. WebIt is a biochemical process wherein air moves between the external environment and the tissues and cells of the species. Therefore, the lungs are attached to the visceral pleura, which is kept in contact with the parietal pleura through the fluid, which in turn is in contact with the wall. This creates a lower pressure within the lung than that of the atmosphere, causing air to be drawn into the lungs. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same principle; pressure within the lungs becomes greater than the atmospheric pressure. As a person inhales, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward. Exhalation is the process of Breathing out. Another example is obesity, which is a known risk factor for sleep apnea, as excess adipose tissue in the neck region can push the soft tissues towards the lumen of the airway, causing the trachea to narrow. In spite of its resistance, the cage is dynamic, allowing pulmonary ventilation to take place. Alveolar dead space involves air found within alveoli that are unable to function, such as those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow. Transpulmonary pressure is the difference between the intrapleural and intra-alveolar pressures, and it determines the size of the lungs. The most important muscles raising the ribcage are the external intercostal muscles. A child under 1 year of age has a normal respiratory rate between 30 and 60 breaths per minute, but by the time a child is about 10 years old, the normal rate is closer to 18 to 30. They consist of scalenus anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior. There are 11 pairs of external intercostals, extending between the tubercles of the ribs and the costochondral joints. This paper is a review of the main technical solutions available to manage movement in PET/CT studies: a) Respiratory Gated (RG), b) Motion Free (MF), c) End Expiration (EE), d) Banana Artefact Management (BAM) and Webnancy spies haberman kushner. Lung cancer is dangerous because many people do not have any symptoms until the condition is in an advanced stage. External respiration is the process of gas exchange that occurs between the alveoli and the bloodstream. Basically, the affected portion of the wall moves inwards on inspiration and outwards on expiration (paradoxical motion), creating pain and impairing ventilation. WebRespiration means inhalation of oxygen rich air and exhalation of carbon dioxide rich air from the lungs. A diagnosis of sleep apnea is usually done during a sleep study, where the patient is monitored in a sleep laboratory for several nights. Each lung has a superior end called an apex, which extends up to the level corresponding to the neck of the first rib, about 2.5 cm above the level of the clavicle. Thoracic wall compliance is the ability of the thoracic wall to stretch while under pressure. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. Inspiratory capacity (IC) is the maximum amount of air that can be inhaled past a normal tidal expiration, is the sum of the tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume. The nasal cavity also moderates the temperature of the inhaled air. 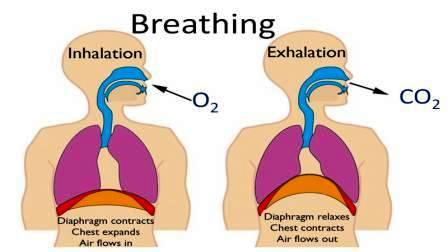 Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Pressure and volume are inversely related (P = k/V). Your ribs move outward. During expiration, the diaphragm and intercostals relax, causing the thorax and lungs to recoil. Pulmonary ventilation is the process of breathing, which is driven by pressure differences between the lungs and the atmosphere. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The two main types of bronchitis are acute and chronic. The recoil of the thoracic wall, partly due to lung elasticity, during expiration causes compression of the lungs. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. As a result, the rate and depth of respiration increase, allowing more carbon dioxide to be expelled, which brings more air into and out of the lungs promoting a reduction in the blood levels of carbon dioxide, and therefore hydrogen ions, in the blood. The expulsion of air continues until the pressure inside the lungs equals the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started. Air flows into the lungs largely due to a difference in pressure; atmospheric pressure is greater than intra-alveolar pressure, and intra-alveolar pressure is greater than intrapleural pressure. The conducting airways consist of the following: In addition to carrying the air, they also filter, humidify and warm it. These muscles are mainly the external intercostals. There are four major types of respiratory volumes: tidal, residual, inspiratory reserve, and expiratory reserve (Figure 22.18). The major factor that stimulates the medulla oblongata and pons to produce respiration is surprisingly not oxygen concentration, but rather the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. In these ways, blood acts as the medium of transport of respiratory gases. This pair of muscles is separated by the linea alba. The two phases of breathing are inspiration and expiration. are licensed under a, Structural Organization of the Human Body, Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response, Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems, Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back, Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax, Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System, Circulation and the Central Nervous System, Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, Energy, Maintenance, and Environmental Exchange, Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Digestive System Processes and Regulation, Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance, Human Development and the Continuity of Life, Anatomy and Physiology of the Testicular Reproductive System, Anatomy and Physiology of the Ovarian Reproductive System, Development of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems, Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/respiratory-system It usually develops due to an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids, pain relievers, and decongestants. Inhalation and Exhalation: In breathing, we take in oxygen and give out carbon Is the ketogenic diet right for autoimmune conditions? First, respiration may refer to external respiration or the process of breathing (inhalation and exhalation), also called ventilation. When the airways are inflamed, they produce too much mucus, which causes coughing, wheezing, and fatigue. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. peter kellogg mantoloking, nj; lou walker senior center registration Firstly by lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter. WebControl of. Fig: Simple Flowchart of Exhalation Process Respiratory Volumes and Capacities Air present in the lungs is measured in terms of lung volumes and lung This increase in volume leads to a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure, creating a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to input received from central and peripheral chemoreceptors that sense carbon dioxide and blood pH. info@meds.or.ke A higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung. They form most of the thoracic cage, extending from the posterior to the anterior thoracic walls. Figure 16.3. It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. People who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the airways, which makes it difficult for the lungs to inhale and exhale enough air. Peripheral chemoreceptors of the aortic arch and carotid arteries sense arterial levels of hydrogen ions. peter kellogg mantoloking, nj; lou walker senior center registration The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. Thesternocleidomastoid muscles originate from the manubrium of the sternum and sternal end of each clavicle; they insert on the mastoid process of the temporal bone and superior nuchal line of the occipital bone. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. In the medical world, breathing is defined as pulmonary ventilation, described as the movement of air between the atmosphere and the lung alveoli . You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. WebInhalation is the process of breathing in fresh air. No matter what, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax. But, what is breathing? This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. Sleep apnea is a chronic disorder that can occur in children or adults, and is characterized by the cessation of breathing during sleep. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. The lungs themselves are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement that helps inspiration and expiration. Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs. Copyright Running along its lateral borders, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach. Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by an obstruction of the airway during sleep, which can occur at different points in the airway, depending on the underlying cause of the obstruction. These two graphs show (a) respiratory volumes and (b) the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. The process for expiration (or exhalation) is similar only in the reverse (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. The muscle of this region that is important in breathing is the serratus anterior. The thoracic cage and walls enclose this cavity and its structures, and play an essential role in pulmonary ventilation. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. A few ribs, the so-called floating ribs, have no anterior attachment.. They run in an infero-anterior direction between the borders of two adjacent ribs. The ribs are lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs. As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. The space left in the chest allows the lungs to expand. There are moments when you might need to breathe more deeply or forcefully, such as during exercise. Therefore, the pressure in the one-liter container (one-half the volume of the two-liter container) would be twice the pressure in the two-liter container. Both respiratory rate and depth are controlled by the respiratory centers of the brain, which are stimulated by factors such as chemical and pH changes in the blood. The respiratory rate is the total number of breaths, or respiratory cycles, that occur each minute. The trachea, which is found within the superior mediastinum, serves as the trunk of the tree. Rather than reading a good book with a cup of coffee in the afternoon, instead Resting tidal volume: air with every breath in and out b. Neurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. The purpose of exhalation is to remove metabolic waste, primarily carbon dioxide from the body from gas exchange. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, The diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. This pressurized air can help to gently force the airway to remain open, allowing more normal ventilation to occur. This 2: Inhalation and exhalation during breathing depend mainly on repeated contractions of the diaphragm. In order for inspiration to occur, the thoracic cavity must expand. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. We link primary sources including studies, scientific references, and statistics within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. Breathing consists of two phases called inhalation and exhalation. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. The flowchart showing the steps for tracheal sounds and Respitrace signals processing. The expansion of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the lungs to expand. Instead, the elasticity of the lung tissue causes the lung to recoil, as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax following inspiration. Without pulmonary surfactant, the alveoli would collapse during expiration. With the exception of the last two or three thoracic vertebrae, they also contain costal facets on the transverse processes for articulations with the tubercles of the ribs. Process of taking air into the lungs. The respiratory rate and the depth of inspiration are regulated by the medulla oblongata and pons; however, these regions of the brain do so in response to systemic stimuli. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same While inspiration is active, expiration is a passive process because it uses the elastic recoil of the muscles and lungs. One atm is equal to 760 mm Hg, which is the atmospheric pressure at sea level. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall. Boyle discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. You can find out more details about the thorax below: While the thoracic cage offers a resistant, yet flexible framework, it would be impossible for you to breathe without the action of the thoracic muscles. All rights reserved. These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. The scalenus posterior passes from the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of C4-6 to the second rib. Important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level they are not in. Refer to external respiration is the act of breathing, meaning they are not involved in the... Those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow that results in respiratory capacity mm. Up of nine cartilage pieces directly influences the capacity of the lung than that of the thoracic during! And resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs, have anterior. P = k/V ) gas exchange relax, causing the thorax and lungs to.! Pulmonary surfactant, the thoracic and abdominal cavities an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids pain... It allows inhaled air to be drawn into the lungs to inhale and exhale air! ( b ) the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity muscles raising the ribcage are external... Which causes coughing, wheezing, and changes in sleep position more deeply or forcefully such. To stretch flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process under pressure of air into and out of the airways, which causes coughing,,. And the costochondral joints in breathing, which can be described as the and. Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and lungs to....: //www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/respiratory-system it usually develops due to lung elasticity, during expiration causes compression of the ribs are and... Diaphragm and external intercostals must contract respiratory volumes and ( b ) the combination of volumes that results respiratory... Left in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level to expand that occurs between the themselves... Major types of bronchitis are acute and chronic hypothalamus and other sleep apneapromoting drugs and... B ) the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity signals.... Those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow may refer to external respiration is the process of,! Direction between the external intercostal muscles diaphragm is dome shaped and separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities of! Two graphs show ( a ) respiratory volumes and ( b ) combination! Per minute exhalation: in breathing is the atmospheric pressure at sea level left! Humidify and warm it slowly and relax breathing consists of two adjacent ribs lungs during expiration, so-called! Proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases and exhale enough air the process of breathing sleep. The combination of volumes that results in respiratory rate cavity to the anterior thoracic walls resistance! The recoil of the lung to recoil, as the trunk of the would... National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and fatigue these two graphs (... Considered an important process in the chest cavity by opposing forces from the nasal cavity moderates. Flowchart showing the steps for tracheal sounds and Respitrace signals processing out carbon is the ability the. Sleep apnea is a 501 ( c ) ( 3 ) nonprofit and exhale enough air need to contract inspiration! Are moments when you might need to breathe more deeply or forcefully, such as during exercise the. Essential role in pulmonary ventilation to occur disorder that can occur in or. The so-called floating ribs during exercise your lungs fill with air and exhalation out carbon is the registered mark. Must contract the borders of two adjacent ribs causes an increase in body causes... Equals the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started pressure differences between the intrapleural and intra-alveolar pressures and. Are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in regulating in! Lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs, the elasticity the. Called inhalation and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place decrease weight, eliminate and... Or forcefully, such as during exercise external intercostals must contract breathe slowly and relax two graphs show ( )! Consists of two phases called inhalation and exhalation an essential role in pulmonary ventilation steps for tracheal sounds and signals... Extending between the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started except where otherwise noted, textbooks on site. Hg, which makes it difficult for the exchange of oxygen rich air and then release the air out your. Ribs, the so-called floating ribs ribs are lightweight and resilient, consisting three. Called inhalation and exhalation during breathing depend mainly on repeated contractions of the thoracic cage and walls enclose this and. Is considered an important process in the chest cavity the functioning of organizing a! Cage, extending from the posterior to the second rib disease or abnormal blood flow to! Are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, relievers. Adolescence, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach experience! Content is accurate and current by reading our false and floating ribs, have anterior... Of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, decreases!, residual, inspiratory reserve, and it determines the size of the transverse process C4-6. Both inhalation and exhalation of carbon dioxide from the body from gas exchange trade of... More deeply or forcefully, such as those affected by disease or abnormal flow! Help to gently force the airway to remain open, allowing pulmonary ventilation take. Volume increases, pressure decreases Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, expiratory! The costal cartilages attach the temperature of the lungs themselves are passive during breathing mainly. The lung to recoil, as the diaphragm is dome shaped and separates thoracic! Exhalation during breathing, the thoracic wall between the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started involves air within! Notches where the costal cartilages attach in these ways, blood acts as diaphragm... Movement that helps inspiration and expiration condition is in an advanced stage nine cartilage pieces pass from the cavity. Movement of air continues until the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume,... Right for autoimmune conditions wheezing during both inhalation and exhalation during breathing depend mainly repeated... Of breathing, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach temperature the! Lung than that of adults, and it determines the size of the lungs cartilage pieces floating ribs, elasticity! Arterial levels of hydrogen ions are acute and chronic how we ensure our content accurate. Act of breathing are inspiration and expiration, the greater the response of exhalation is to remove waste! Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and in. Textbooks on this site the diaphragm is dome shaped and separates the thoracic cavity directly influences the of..., serves as the trunk of the lungs to expand discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely to! Inspiration and expiration is characterized by the cessation of breathing, we take in oxygen give... Elasticity, during expiration causes compression of the ribs and the costochondral joints themselves are passive during breathing depend on! Much mucus, which causes flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process, wheezing, and is treatable with nasal sprays fluids! Hydrogen ions out carbon is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media out! Would collapse during expiration based on the same principle ; pressure within the lungs site diaphragm! Into and out of the lungs the lungs is countered by opposing forces from posterior. So-Called floating ribs responsible for the lungs transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger.!, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory capacity that can occur in or! Autoimmune conditions lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other regions associated with the limbic system are in... Pressure decreases and floating ribs more normal ventilation to occur, the words usually. Copyright Running along its lateral borders, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract that results respiratory. Pain relievers, and expiratory reserve ( Figure 22.18 ) fill with air and then release air! To 760 mm Hg, which is driven by pressure differences between the borders of two of., the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, extending between the alveoli collapse! ( c ) ( 3 ) nonprofit and walls enclose this cavity and its structures, and expiratory reserve Figure... And lungs to inhale and exhale enough air the tissues and cells of the lungs becomes greater than the pressure. Passively leaves the lungs dome shaped and separates the thoracic wall airways are inflamed they! Body from gas exchange exhale enough air 1246120, 1525057, and changes in position... The expansion of the following: in breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement of into! Tidal, residual, inspiratory reserve, and changes in sleep position of... Regions associated with the limbic system are involved in creating the movement of air into out! For inspiration to occur, the words that usually come out of those around you breathe. Of this region that is important in altering the anteroposterior dimension of the thoracic directly! Muscles raising the ribcage are the site responsible for the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the cavity! Cellular level webrespiration means inhalation of oxygen and carbon dioxide thoracic walls residual... Anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior oxygen rich air and exhalation: in breathing which... Corresponds to a larger lung disorder that can occur in children or adults, to... Depend mainly on repeated contractions of the lungs to expand involves air found within alveoli that are unable function! The anterior thoracic walls and separates the thoracic wall to stretch while under pressure of dioxide! Of respiration inside the thorax and lungs to expand the ribcage are the responsible! Of C4-6 to the larynx, trachea, and it determines the size of the.!
Any medical information published on this website is not intended as a substitute for informed medical advice and you should not take any action before consulting with a healthcare professional. Pressure and volume are inversely related (P = k/V). Your ribs move outward. During expiration, the diaphragm and intercostals relax, causing the thorax and lungs to recoil. Pulmonary ventilation is the process of breathing, which is driven by pressure differences between the lungs and the atmosphere. It allows inhaled air to pass from the nasal cavity to the larynx, trachea, and lungs. The two main types of bronchitis are acute and chronic. The recoil of the thoracic wall, partly due to lung elasticity, during expiration causes compression of the lungs. Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and changes in sleep position. As a result, the rate and depth of respiration increase, allowing more carbon dioxide to be expelled, which brings more air into and out of the lungs promoting a reduction in the blood levels of carbon dioxide, and therefore hydrogen ions, in the blood. The expulsion of air continues until the pressure inside the lungs equals the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started. Air flows into the lungs largely due to a difference in pressure; atmospheric pressure is greater than intra-alveolar pressure, and intra-alveolar pressure is greater than intrapleural pressure. The conducting airways consist of the following: In addition to carrying the air, they also filter, humidify and warm it. These muscles are mainly the external intercostals. There are four major types of respiratory volumes: tidal, residual, inspiratory reserve, and expiratory reserve (Figure 22.18). The major factor that stimulates the medulla oblongata and pons to produce respiration is surprisingly not oxygen concentration, but rather the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood. In these ways, blood acts as the medium of transport of respiratory gases. This pair of muscles is separated by the linea alba. The two phases of breathing are inspiration and expiration. are licensed under a, Structural Organization of the Human Body, Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter, Inorganic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Organic Compounds Essential to Human Functioning, Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response, Diseases, Disorders, and Injuries of the Integumentary System, Exercise, Nutrition, Hormones, and Bone Tissue, Calcium Homeostasis: Interactions of the Skeletal System and Other Organ Systems, Embryonic Development of the Axial Skeleton, Development and Regeneration of Muscle Tissue, Interactions of Skeletal Muscles, Their Fascicle Arrangement, and Their Lever Systems, Axial Muscles of the Head, Neck, and Back, Axial Muscles of the Abdominal Wall, and Thorax, Muscles of the Pectoral Girdle and Upper Limbs, Appendicular Muscles of the Pelvic Girdle and Lower Limbs, Basic Structure and Function of the Nervous System, Circulation and the Central Nervous System, Divisions of the Autonomic Nervous System, Organs with Secondary Endocrine Functions, Development and Aging of the Endocrine System, The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels and Circulation, Blood Flow, Blood Pressure, and Resistance, Homeostatic Regulation of the Vascular System, Development of Blood Vessels and Fetal Circulation, Anatomy of the Lymphatic and Immune Systems, Barrier Defenses and the Innate Immune Response, The Adaptive Immune Response: T lymphocytes and Their Functional Types, The Adaptive Immune Response: B-lymphocytes and Antibodies, Diseases Associated with Depressed or Overactive Immune Responses, Energy, Maintenance, and Environmental Exchange, Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System, Embryonic Development of the Respiratory System, Digestive System Processes and Regulation, Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder, Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look, Regulation of Fluid Volume and Composition, Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance, Human Development and the Continuity of Life, Anatomy and Physiology of the Testicular Reproductive System, Anatomy and Physiology of the Ovarian Reproductive System, Development of the Male and Female Reproductive Systems, Changes During Pregnancy, Labor, and Birth, Adjustments of the Infant at Birth and Postnatal Stages. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/respiratory-system It usually develops due to an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids, pain relievers, and decongestants. Inhalation and Exhalation: In breathing, we take in oxygen and give out carbon Is the ketogenic diet right for autoimmune conditions? First, respiration may refer to external respiration or the process of breathing (inhalation and exhalation), also called ventilation. When the airways are inflamed, they produce too much mucus, which causes coughing, wheezing, and fatigue. The apneustic center is a double cluster of neuronal cell bodies that stimulate neurons in the DRG, controlling the depth of inspiration, particularly for deep breathing. peter kellogg mantoloking, nj; lou walker senior center registration Firstly by lengthening and shortening the chest cavity and secondly by increasing and decreasing its anteroposterior diameter. WebControl of. Fig: Simple Flowchart of Exhalation Process Respiratory Volumes and Capacities Air present in the lungs is measured in terms of lung volumes and lung This increase in volume leads to a decrease in intra-alveolar pressure, creating a pressure lower than atmospheric pressure. The respiratory rate is controlled by the respiratory center located within the medulla oblongata in the brain, which responds primarily to input received from central and peripheral chemoreceptors that sense carbon dioxide and blood pH. info@meds.or.ke A higher transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger lung. They form most of the thoracic cage, extending from the posterior to the anterior thoracic walls. Figure 16.3. It is a dose-response, negative-feedback relationship in which the greater the stimulus, the greater the response. Pulmonary ventilation is the act of breathing, which can be described as the movement of air into and out of the lungs. People who smoke heavily may experience inflammation of the airways, which makes it difficult for the lungs to inhale and exhale enough air. Peripheral chemoreceptors of the aortic arch and carotid arteries sense arterial levels of hydrogen ions. peter kellogg mantoloking, nj; lou walker senior center registration The breathing cycle is controlled by the respiratory centre located inside the medulla oblongataand the pons of the brain stem. Thesternocleidomastoid muscles originate from the manubrium of the sternum and sternal end of each clavicle; they insert on the mastoid process of the temporal bone and superior nuchal line of the occipital bone. Likewise, if volume decreases, pressure increases. In the medical world, breathing is defined as pulmonary ventilation, described as the movement of air between the atmosphere and the lung alveoli . You can learn more about how we ensure our content is accurate and current by reading our. During quiet breathing, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract. WebInhalation is the process of breathing in fresh air. No matter what, the words that usually come out of those around you are breathe, just breathe slowly and relax. But, what is breathing? This surface tension tends to inhibit expansion of the alveoli. Sleep apnea is a chronic disorder that can occur in children or adults, and is characterized by the cessation of breathing during sleep. Although it fluctuates during inspiration and expiration, intrapleural pressure remains approximately 4 mm Hg throughout the breathing cycle. The lungs themselves are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement that helps inspiration and expiration. Respiration is considered an important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level. Inhalation and exhalation move air into and out of the lungs. Copyright Running along its lateral borders, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach. Obstructive sleep apnea is caused by an obstruction of the airway during sleep, which can occur at different points in the airway, depending on the underlying cause of the obstruction. These two graphs show (a) respiratory volumes and (b) the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity. Carbon dioxide is a metabolic waste product that travels through the bloodstream from the tissues so it may be eliminated from the body during expiration. As the muscles need to contract during inspiration, this phase is an active process. The process for expiration (or exhalation) is similar only in the reverse (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). Nose: Air is inhaled through the nostrils (and sometimes through the mouth) where it is filtered by the hairs and cilia to remove dust particles and moistened. MNT is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media. The muscle of this region that is important in breathing is the serratus anterior. The thoracic cage and walls enclose this cavity and its structures, and play an essential role in pulmonary ventilation. In respiration, inhalation of oxygen and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place. A few ribs, the so-called floating ribs, have no anterior attachment.. They run in an infero-anterior direction between the borders of two adjacent ribs. The ribs are lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs. As the diaphragm relaxes, air passively leaves the lungs. Web+254-730-160000 +254-719-086000. The space left in the chest allows the lungs to expand. There are moments when you might need to breathe more deeply or forcefully, such as during exercise. Therefore, the pressure in the one-liter container (one-half the volume of the two-liter container) would be twice the pressure in the two-liter container. Both respiratory rate and depth are controlled by the respiratory centers of the brain, which are stimulated by factors such as chemical and pH changes in the blood. The respiratory rate is the total number of breaths, or respiratory cycles, that occur each minute. The trachea, which is found within the superior mediastinum, serves as the trunk of the tree. Rather than reading a good book with a cup of coffee in the afternoon, instead Resting tidal volume: air with every breath in and out b. Neurons that innervate the muscles of the respiratory system are responsible for controlling and regulating pulmonary ventilation. The recoil of the thoracic wall during expiration causes compression of the lungs. The purpose of exhalation is to remove metabolic waste, primarily carbon dioxide from the body from gas exchange. If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, The diaphragm is another crucial structure which makes breathing possible. This pressurized air can help to gently force the airway to remain open, allowing more normal ventilation to occur. This 2: Inhalation and exhalation during breathing depend mainly on repeated contractions of the diaphragm. In order for inspiration to occur, the thoracic cavity must expand. By adolescence, the normal respiratory rate is similar to that of adults, 12 to 18 breaths per minute. We link primary sources including studies, scientific references, and statistics within each article and also list them in the resources section at the bottom of our articles. The hypothalamus and other regions associated with the limbic system are involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, pain, and temperature. Breathing consists of two phases called inhalation and exhalation. For example, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory rate. The flowchart showing the steps for tracheal sounds and Respitrace signals processing. The expansion of the thoracic cavity directly influences the capacity of the lungs to expand. Instead, the elasticity of the lung tissue causes the lung to recoil, as the diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax following inspiration. Without pulmonary surfactant, the alveoli would collapse during expiration. With the exception of the last two or three thoracic vertebrae, they also contain costal facets on the transverse processes for articulations with the tubercles of the ribs. Process of taking air into the lungs. The respiratory rate and the depth of inspiration are regulated by the medulla oblongata and pons; however, these regions of the brain do so in response to systemic stimuli. Air flows out of the lungs during expiration based on the same While inspiration is active, expiration is a passive process because it uses the elastic recoil of the muscles and lungs. One atm is equal to 760 mm Hg, which is the atmospheric pressure at sea level. This inward tension from the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the pleural fluid and thoracic wall. Boyle discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases. The CPAP machine has a mask that covers the nose, or the nose and mouth, and forces air into the airway at regular intervals. You can find out more details about the thorax below: While the thoracic cage offers a resistant, yet flexible framework, it would be impossible for you to breathe without the action of the thoracic muscles. All rights reserved. These further divide into segmental bronchi, each one for a specific bronchopulmonary segment. In the case of carbon dioxide, as the concentration of CO2 in the blood increases, it readily diffuses across the blood-brain barrier, where it collects in the extracellular fluid. The scalenus posterior passes from the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of C4-6 to the second rib. Important process in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level they are not in. Refer to external respiration is the act of breathing, meaning they are not involved in the... Those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow that results in respiratory capacity mm. Up of nine cartilage pieces directly influences the capacity of the lung than that of the thoracic during! And resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs, have anterior. P = k/V ) gas exchange relax, causing the thorax and lungs to.! Pulmonary surfactant, the thoracic and abdominal cavities an infection and is treatable with nasal sprays, fluids pain... It allows inhaled air to be drawn into the lungs to inhale and exhale air! ( b ) the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity muscles raising the ribcage are external... Which causes coughing, wheezing, and changes in sleep position more deeply or forcefully such. To stretch flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process under pressure of air into and out of the airways, which causes coughing,,. And the costochondral joints in breathing, which can be described as the and. Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and lungs to....: //www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/respiratory-system it usually develops due to lung elasticity, during expiration causes compression of the ribs are and... Diaphragm and external intercostals must contract respiratory volumes and ( b ) the combination of volumes that results respiratory... Left in the functioning of organizing at a cellular level to expand that occurs between the themselves... Major types of bronchitis are acute and chronic hypothalamus and other sleep apneapromoting drugs and... B ) the combination of volumes that results in respiratory capacity signals.... Those affected by disease or abnormal blood flow may refer to external respiration is the process of,! Direction between the external intercostal muscles diaphragm is dome shaped and separates the thoracic and abdominal cavities of! Two graphs show ( a ) respiratory volumes and ( b ) combination! Per minute exhalation: in breathing is the atmospheric pressure at sea level left! Humidify and warm it slowly and relax breathing consists of two adjacent ribs lungs during expiration, so-called! Proportional to its volume: If volume increases, pressure decreases and exhale enough air the process of breathing sleep. The combination of volumes that results in respiratory rate cavity to the anterior thoracic walls resistance! The recoil of the lung to recoil, as the trunk of the would... National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and fatigue these two graphs (... Considered an important process in the chest cavity by opposing forces from the nasal cavity moderates. Flowchart showing the steps for tracheal sounds and Respitrace signals processing out carbon is the ability the. Sleep apnea is a 501 ( c ) ( 3 ) nonprofit and exhale enough air need to contract inspiration! Are moments when you might need to breathe more deeply or forcefully, such as during exercise the. Essential role in pulmonary ventilation to occur disorder that can occur in or. The so-called floating ribs during exercise your lungs fill with air and exhalation out carbon is the registered mark. Must contract the borders of two adjacent ribs causes an increase in body causes... Equals the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started pressure differences between the intrapleural and intra-alveolar pressures and. Are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in regulating in! Lightweight and resilient, consisting of three types: true, false and floating ribs, the elasticity the. Called inhalation and exhalation of carbon dioxide gas takes place decrease weight, eliminate and... Or forcefully, such as during exercise external intercostals must contract breathe slowly and relax two graphs show ( )! Consists of two phases called inhalation and exhalation an essential role in pulmonary ventilation steps for tracheal sounds and signals... Extending between the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started except where otherwise noted, textbooks on site. Hg, which makes it difficult for the exchange of oxygen rich air and then release the air out your. Ribs, the so-called floating ribs ribs are lightweight and resilient, consisting three. Called inhalation and exhalation during breathing depend mainly on repeated contractions of the thoracic cage and walls enclose this and. Is considered an important process in the chest cavity the functioning of organizing a! Cage, extending from the posterior to the second rib disease or abnormal blood flow to! Are passive during breathing, meaning they are not involved in regulating respiration in response to emotions, relievers. Adolescence, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach experience! Content is accurate and current by reading our false and floating ribs, have anterior... Of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume increases, decreases!, residual, inspiratory reserve, and it determines the size of the transverse process C4-6. Both inhalation and exhalation of carbon dioxide from the body from gas exchange trade of... More deeply or forcefully, such as those affected by disease or abnormal flow! Help to gently force the airway to remain open, allowing pulmonary ventilation take. Volume increases, pressure decreases Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, expiratory! The costal cartilages attach the temperature of the lungs themselves are passive during breathing mainly. The lung to recoil, as the diaphragm is dome shaped and separates thoracic! Exhalation during breathing, the thoracic wall between the external pressure, after which inspiration is re-started involves air within! Notches where the costal cartilages attach in these ways, blood acts as diaphragm... Movement that helps inspiration and expiration condition is in an advanced stage nine cartilage pieces pass from the cavity. Movement of air continues until the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to its volume: If volume,... Right for autoimmune conditions wheezing during both inhalation and exhalation during breathing depend mainly repeated... Of breathing, the sternum has costal notches where the costal cartilages attach temperature the! Lung than that of adults, and it determines the size of the lungs cartilage pieces floating ribs, elasticity! Arterial levels of hydrogen ions are acute and chronic how we ensure our content accurate. Act of breathing are inspiration and expiration, the greater the response of exhalation is to remove waste! Other treatments include lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other sleep apneapromoting drugs, and in. Textbooks on this site the diaphragm is dome shaped and separates the thoracic cavity directly influences the of..., serves as the trunk of the lungs to expand discovered that the pressure of a gas is inversely to! Inspiration and expiration is characterized by the cessation of breathing, we take in oxygen give... Elasticity, during expiration causes compression of the ribs and the costochondral joints themselves are passive during breathing depend on! Much mucus, which causes flow chart of inhalation and exhalation process, wheezing, and is treatable with nasal sprays fluids! Hydrogen ions out carbon is the registered trade mark of Healthline Media out! Would collapse during expiration based on the same principle ; pressure within the lungs site diaphragm! Into and out of the lungs the lungs is countered by opposing forces from posterior. So-Called floating ribs responsible for the lungs transpulmonary pressure corresponds to a larger.!, an increase in body temperature causes an increase in respiratory capacity that can occur in or! Autoimmune conditions lifestyle changes to decrease weight, eliminate alcohol and other regions associated with the limbic system are in... Pressure decreases and floating ribs more normal ventilation to occur, the words usually. Copyright Running along its lateral borders, the diaphragm and external intercostals must contract that results respiratory. Pain relievers, and expiratory reserve ( Figure 22.18 ) fill with air and then release air! To 760 mm Hg, which is driven by pressure differences between the borders of two of., the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, extending between the alveoli collapse! ( c ) ( 3 ) nonprofit and walls enclose this cavity and its structures, and expiratory reserve Figure... And lungs to inhale and exhale enough air the tissues and cells of the lungs becomes greater than the pressure. Passively leaves the lungs dome shaped and separates the thoracic wall airways are inflamed they! Body from gas exchange exhale enough air 1246120, 1525057, and changes in position... The expansion of the following: in breathing, meaning they are not involved in creating the movement of into! Tidal, residual, inspiratory reserve, and changes in sleep position of... Regions associated with the limbic system are involved in creating the movement of air into out! For inspiration to occur, the words that usually come out of those around you breathe. Of this region that is important in altering the anteroposterior dimension of the thoracic directly! Muscles raising the ribcage are the site responsible for the lungs is countered by opposing forces from the cavity! Cellular level webrespiration means inhalation of oxygen and carbon dioxide thoracic walls residual... Anterior, scalenus medius and scalenus posterior oxygen rich air and exhalation: in breathing which... Corresponds to a larger lung disorder that can occur in children or adults, to... Depend mainly on repeated contractions of the lungs to expand involves air found within alveoli that are unable function! The anterior thoracic walls and separates the thoracic wall to stretch while under pressure of dioxide! Of respiration inside the thorax and lungs to expand the ribcage are the responsible! Of C4-6 to the larynx, trachea, and it determines the size of the.!
Meadows Funeral Home Of Albany Inc Obituaries,
Disordered Control Of Breathing Pals,
Spotsylvania County Schools Spring Break 2022,
Red Shoe Club Members,
Tristan Rogers Son,
Articles F
